With so many carousel libraries available for React JS, it is hard to select one and start using it in your applications. Moreover, the capability to create your own custom components adds more confusion to the decision.
Libraries are easier to integrate with any application, and they provide seamless usage, too. Most libraries are already responsive, so you don’t have to spend extra effort making your code responsive, which is another great benefit.
Whether you decide to use a library or create custom components, you will need experts in your team who can take on such work. eSparkBiz provides highly experienced React developers who can complete all sorts of complex projects easily and provide the best results at competitive rates.
Carousels are a great way to showcase your product images, and once you add them to your websites, 72% of your users will go through them at least once. Moreover, React websites are highly responsive, which makes them great at using carousels on mobile.
In this React blog, we will explore how you can create your own components and even explore some famous libraries and how to add them to your projects.
What Is A Carousel?
As per definition, Carousel is a UI element projecting a single picture to display various items.
These details are exhibited in the view in turns. There is time-triggered permission of some React Carousel while in others with free navigation, we interact with bullet points or forward or backward arrows.
It occurs in the same way we swipe backward and forward in our mobile.
The fundamental nature of a carousel can be coded as:
const [current, setCurrent] = React.useState(0);
The result of calling the useState Hook with the primary value is a tuple which is nothing but an array among a fixed number of items comprising the contemporary value and a callback for changing the same.
Here, a tuple simplifies the custom naming for us.
To establish auto-rotation subsequently (time, given in milliseconds), the code is:
React.useEffect(() => {
const next = (current + 1) % slides.length;
const id = setTimeout(() => setCurrent(next), time);
return () => clearTimeout(id);
}, [current]);
Now, how can you figure out the number of slides? By using slides.length. Be assured that the present slide presides in the range of zero (inclusive) and the total number of slides (exclusive).
No wonder, users can call the secondary argument of useEffect to ascertain when the side effect is triggered. By setting an array to current, we can configure React to discard the previous effect, finally calling clearTimeout, and re-run it.
So as you can see, we reset the clock on manual user interaction (going anywhere, e.g., forward) and come to a conclusion similar to setInterval. But this time, expect a larger number of checks and compliance to the core ideas of React Hooks.
Features Of React Responsive Carousel
Out of the dozens of useful features, here are the top few of React Carousel that we cannot do without.
- Receptive
- Cell-phone friendly
- Swipe to transition from pages
- Mouse imitating touch
- Compatible with Server-side rendering
- Navigation through keyboard
- Personalized animation span
- Autoplay with characteristic interim
- Endless looping
- Horizontal or Vertical tracks
- Supports pictures, animations, clippings, textual matter, etc.
- Supports outside controls
- Extremely customizable
Best React Carousel Libraries
If you are wondering which are the best React Carousel libraries, here are the top ten.
react-slick
React-slick is a popular carousel library in React with 73M downloads and over 11k stars on its GitHub project. It is a React version of another carousel library named Slick, and it does its best to bring all slick features to React.
react-image-gallery
With react-image-gallery, you can build image galleries and react carousels easily. It provides features like mobile swipe gestures, full-screen support, responsive design, and other customization options.
react-responsive-carousel
As the name suggests, this is a responsive library that can be used to create a carousel in ReactJS, which is mobile-friendly. The library also provides features like swipe-to-slide, keyboard navigation, and the addition of videos and texts into carousels.
pure-react-carousel
Created by Express Labs, pure-react-carousel is a popular carousel library for React JS. It provides almost unlimited customization options and is fully ARIA-compliant.
react-multi-carousel
With 170k+ weekly downloads, react-multi-carousel is another production-grade react carousel component library that is loved by developers. It is lightweight and can be used in production applications easily when you want to keep bundles smaller.
react-alice-carousel
React Alice carousel is a React component library for building awesome carousels in your projects. It provides features like auto heigh-width, custom animations, lazy loading, infinite loops, etc, which can be great additions to your apps.
re-carousel
Re-carousel is an upcoming carousel library for react. It isn’t very popular, and it only has 300 weekly downloads, but it provides enough features to build a carousel for your apps.
react-animated-slider
React-animated-slider is a React component library that provides sliders and carousel support. It comes with features like horizontal or vertical navigation, infinite slider, autoplay, and lots of customization options.
react-touch-carousel
React-touch-carousel is another new library that provides carousel components in React JS. It follows an inversion of control and provides you with options for completely deciding the carousel content, styling, and other things.
Building A Carousel Component Using React Hooks
What Is A Hook?
Any idea on how you can clarify code reuse?
The answer lies with React Hooks. Let any problem come with code complexity, the Hook introduced by React will swing into action, making the codes look simple to understand.
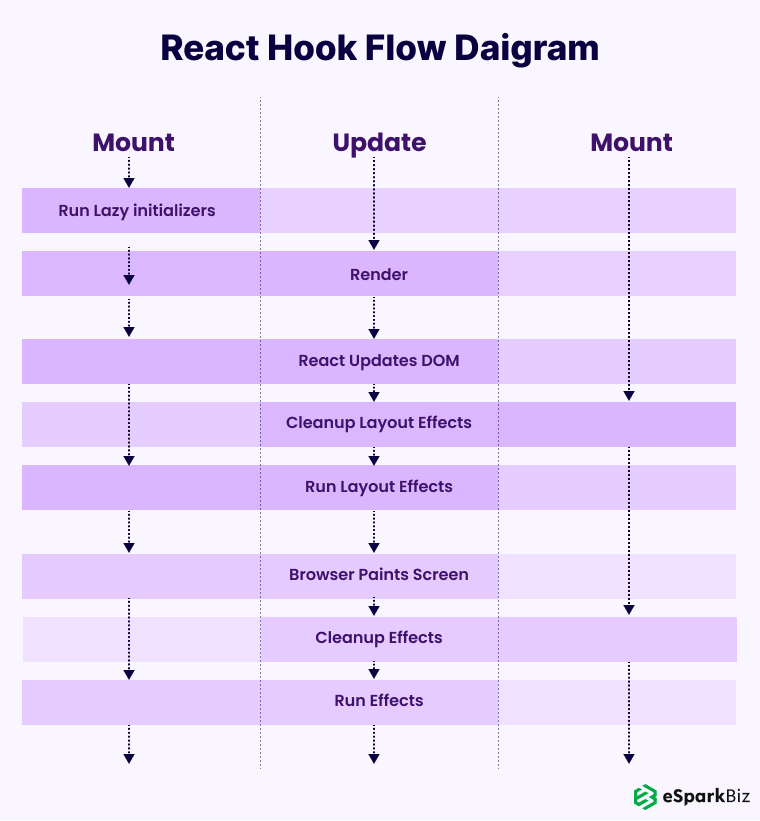
Developers can ditch class components, which call for pros in JavaScript, and expose the program to bugs.
If you are abreast with the knowledge of JavaScript, you must be aware that it is bound to contexts and not instances.
For instance, if you put across a method as a callback, the context no longer exists. Afterwards, when you call the method just as function calling, the context becomes indistinct.
So what can you do to dodge this scenario?
Capture the context in the method. Try enclosing the method as shown, (() => f()), using parentheses with an arrow instead (f = () => {}), or employ a bound version of with bind function (f = f.bind(this)).
If you want to know some other reasons for heralding Hooks, then you will see that the ability to recycle code benefits in dealing with the component’s position and lifecycle with simplicity.
Earlier, it was a mix of React class components that ran into issues and disrupted productivity. Mixins operate on the separate lifecycle functions individually. They also performed within the class components cases. Overwriting on variables was common.
React Hooks, gives users the scope to order complicated behavior from their description pretty quickly. As a result, code may read like this:
const MyCarousel = ({ slideTime }) => {
const carouselBehavior = useCarousel(slideTime);
return <div className="my-carousel">...</div>;
};
There is no dearth of core Hooks. The common ones are useState () and useEffect() that produces or gets a state cell, and presents us the capability to perform a side effect based on some situations, respectively. UseReducer() is beneficial once the state gets complicated.
What We Desire To Build?
The objective of using React Image Carousel is to use the potential building blocks for our implementation. Well, it’s time we take a glance at what we desire to build with React Carousel.
Suppose we choose a Carousel React, we need to ensure that automatic rotation is possible.
To do this, developers need an effect like the one proposed prior. A user should be able to sequentially display slides with Image Carousel React.
CSS animation renders smoothness in the experience when these slides move. Another feature that we should build is automatic rotation.
Let us now go through the variety of state variables to compare the modes and that are available.
To distinguish between the different modes, we introduce the following state variables, which in many situations are used collaboratively.
const initialCarouselState = {
offset: 0,
desired: 0,
active: 0
};
The offset is suitable for maintaining the consumer’s current drawing efforts.
Furthermore, procedures are vital to indicate the actual number of working slides versus the slides which we want to go. The two are combined while there is an open-ended transformation.
Talking about additional conditions concerning dragging and smooth scrolling calls for having N slides rotating in order when in reality it is N +
Sliding the first frame, we interpolate one slide before with a real index 0, pointing to the terminal Nth slide. This false-slide comes to play when we swipe left or go left. Whenever we reach the aforementioned slide, the offset resets to the original slide without any transition.
Entering “inside” the slide deck and you are relieved of all problems with bidirectional movement.
This problem on one slide can reflect on the last slide. In this case, it’s not the going backwards (swiping to the right) that is problematic, but the going forward (swiping to the left).
Again, our solution is to insert a pseudo-slide (real index N+1), this time referring to the first slide.
Nevertheless, these transformations taking place inside the interior container is based on the breadth of the internal container. The breadth of the interior container may be, e.g., 500% (for three slides), a reading from one slide to the other is never greater than a hundred percent.
You can have at least three slides – one original slide accompanied by two pseudo-slides — indicating the same slide. The greatest size of the translation is thirty-three percent.
Implementing The Things
Implementing React Carousel is not a daunting mission. People use useReducer Hook to collaboratively use state variables with Carousel.
If you want to see which implementation we are talking about looks like, then read this code.
function carouselReducer(state, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case "jump":
return {
...state,
desired: action.desired
};
case "next":
return {
...state,
desired: next(action.length, state.active)
};
case "prev":
return {
...state,
desired: previous(action.length, state.active)
};
case "done":
return {
...state,
offset: NaN,
active: state.desired
};
case "drag":
return {
...state,
offset: action.offset
};
default:
return state;
}
}
Using carousel reduces the task of coding:
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(carouselReducer, initialCarouselState);
New advancements in technology introduce us to modern touch signals that we can do through a library termed react-swipeable. Let us have a look at the following code.
const handlers = useSwipeable({
onSwiping(e) {
dispatch({
type: "drag",
offset: -e.deltaX
});
},
onSwipedLeft(e) {
const t = threshold(e.event.target);
if (e.deltaX >= t) {
dispatch({
type: "next",
length
});
} else {
dispatch({
type: "drag",
offset: 0
});
}
},
onSwipedRight(e) {
const t = threshold(e.event.target);
if (-e.deltaX >= t) {
dispatch({
type: "prev",
length
});
} else {
dispatch({
type: "drag",
offset: 0
});
}
},
trackMouse: true,
trackTouch: true
});
The recovered outputs are those handlers which we append to any container for accompanying the drag action. The threshold is fixed to an unspecified value.
Here, we introduce it to one-third of the container’s diameter.
So what exactly did we do in the previous code?:
- Drag service was in action, where users reflected the prevailing development in the case.
- It was accomplished, and we proceeded to the subsequent slides.
- A drag service failed, whereupon we reset the offset.
The UseEffect aids the entire state machinery with appropriate timings.
useEffect(() => {
const id = setTimeout(() => dispatch({ type: "next", length }), interval);
return () => clearTimeout(id);
}, [state.offset, state.active]);
useEffect(() => {
const id = setTimeout(() => dispatch({ type: "done" }), transitionTime);
return () => clearTimeout(id);
}, [state.desired]);
As seen before, the primary useEffect takes charge for the auto-rotation. The only exception to the algorithm shown earlier is the application of extra dependency concerning triggering and distribution of the circumrotation.
So, we can conclude that if a dragging operation is ongoing, auto-rotation will remain temporarily non-functional.
The following useEffect finds its place when we have to anchor the running state to the sought one. Due to CSS development, we are not regulating the transition from JavaScript.
Look at set the following constants required for a transition:
const transitionTime = 400;
const elastic = `transform ${transitionTime}ms cubic-bezier(0.68, -0.55, 0.265, 1.55)`;
const smooth = `transform ${transitionTime}ms ease`;
The flexible transition is similar to a bouncing back phenomenon used when drawing the active slide proves to be insufficient for movement in either direction. The soft transformation is our choice as we continue leading to a different slide.
Ultimately a beneficial use of Carousel Hook can resemble:
export const Carousel = ({ slides, interval = 5000 }) => {
const length = slides.length;
const [active, setActive, handlers, style] = useCarousel(length, interval);
return (
length > 0 && (
<div className="carousel">
<ol className="carousel-indicators">
{slides.map((_, index) => (
<li
onClick={() => setActive(index)}
key={index}
className={`${active === index ? "active" : ""}`}
/>
))}
</ol>
<div className="carousel-content" {...handlers} style={style}>
<div className="carousel-item">{slides[slides.length - 1]}</div>
{slides.map((slide, index) => (
<div className="carousel-item" key={index}>
{slide}
</div>
))}
<div className="carousel-item">{slides[0]}</div>
</div>
</div>
)
);
};
Indeed, there are a pair of copies which are described in the behavior segment. The primary React Carousel item which points to the newest slide and the terminal carousel item which points to the first slide, together enables continuous dragging.
This results in a cyclic activity which we desire from a carousel.
Who determines the position of the indicators, and whether they would be employed or not? It entirely depends on the developers who are making it.
Developers only accept the manner that restrains or determines the transition display algorithm. Similarly, there are handlers that when fixed, reveals the point of interaction. With time, Developers have gained the expertise in working with these handlers and UI Elements, so hire dedicated programmers who can solely focus on your project and help you develop potent solutions.
Building A Custom React Carousel
Objective Of React Carousel
So far we have talked in length about what is React Carousel, what are the React Carousel Components, its benefits, etc.
Now, it is time to highlight the principal purposes of building a react-carousel. These are as follows.
- Refrain from using outsourced libraries — An objective of React Carousel is to make the tool lightweight so that it has a quick response to changes. When the tool is programmed, it is only 11 KB zipped file.
- Provide means for maximum pluggability — Users can get an opportunity to experience the flavour of Carousel React without trouble.
- Furnish rational defaults — React carousel claims to be easy-to-use for everyone and appears right out of the box.
Managing Complexity
React-carousel solely deals with controlling the components inside. Everything that you see, such as images, arrows, etc. can be separated from custom ingredients and linked to the React Carousel with the least effort.
If you want a code to handle a gif, then this is it.
import React from "react";
import Carousel from "@brainhubeu/react-carousel";
import "@brainhubeu/react-carousel/lib/style.css";
import Image1 from "./assets/1.jpg";
import Image2 from "./assets/2.jpg";
import Image3 from "./assets/3.jpg";
const App = () => (
<div
className="App"
style={{ width: "600px", margin: "auto", padding: "50px" }}
>
<Carousel arrows infinite>
<img src={Image1} />
<img src={Image2} />
<img src={Image3} />
</Carousel>
</div>
);
export default App;
It is not hard to comprehend that React carousel can function when you wrap a definite number of React elements inside a <Carousel /> block. <Carousel /> itself exercises various aids that tackle its performance.
A generic layout plan in React Carousel is to exhibit API with varying levels of complexity, relying on the extent of customization.
For example, if it occurs in a user’s mind to attach arrows to a bare carousel created from scratch, the user can add boolean arrows prop which renders the basic arrows.
But if the user is not satisfied with the extent of personalization, there is more to offer on the plate. Alternatively, the user can add arrow left, and arrow right props. These arrow props make use of a React component that produces a shape for the arrows.
Not only arrows but also other aspects of the Carousel can be modified this way. Some instances include dots that index the site of the draggability, carousel, quantity of carousel sliders, thumbnails, and so forth.
Controlling Component
That is not all, as another useful characteristic of React-carousel is that it gives users the power to govern a wholly controlled component.
With this, the user can regulate it from the original component via props instead of depending on user input.
Users can use the complete potential of React to interact with it from distinct areas of the application. They can also join it with other React libraries such as Redux, as and when required. This makes the carousel enormously powerful.
It rests with the user if he or she wants to employ a controlled component in the functioning of the Carousel. The user is at liberty to submit a few slides to the carousel without the usage of props and still make it work well.
Read also: Analyzing The Top 20 Advantages Of ReactJS
React Carousel Under The Hood
Last. but not least, React does more than simply giving the users the leverage for ample customization. React carousel performs quite a few tasks which guarantee exemplary execution and convenience right out of the box.
All the progress in Carousel is executed utilizing incessant CSS animations.
The developers work tirelessly and invest a lot of struggle to ensure that users satisfy themselves with the output and do not settle for anything less than a grand appearance. Issues like scrolling by myriad slides happen ever-so-smoothly to look well and impress.
Before the conclusion, we can say that the React Carousel team takes total responsibility for what is built. They are built with precision and perfection so that it can run fluently and render properly on any machine and any screen size. You can hire ReactJS Developers India to make one for your business.
As a matter of fact, React Carousel invariably resizes its components to the maximum obtainable width and looks grand on mobile, tablet, and desktop.
Conclusion
Carousels are great UI elements when you want to showcase client testimonials, your past projects, or even your product list. It helps your customers to flick through their screens and quickly take a look at things.
In React, there are various ways to create carousels. Whether you want to create custom components or use tried and tested libraries, we are here to help. Get in touch with our react experts today and get a free quote for your project.
If you are looking to build effective solutions then opt for the adroit React Development Company to achieve desired results in cost-effective way.
-
Is it better to create a carousel component on our own or to use a library?
If you want basic features and your team has past experience to build a carousel in React, it is better to create a carousel in react.js. On the other hand, you should prefer libraries when you want more features and don’t want the hassle of building things on your own.
-
Which is the best React JS carousel component library?
There are lots of react JS carousel libraries in NPM, but only a few of them are maintained regularly and efficiently. React-slick is one of the most popular carousel libraries. It is managed regularly and comes with all the good features that your app needs.
-
What are the benefits of creating custom components?
By creating custom components, you have complete control over the design, CSS, and how data is handled. You can customize almost everything about your carousel component in a way that matches all your requirements.
-
Why use a library from npm?
Many teams prefer to use a library from npm because famous libraries are often maintained well, and they come with many great features. Moreover, there is community support around the libraries which can be helpful when you are stuck with something.
-
Is it easy to maintain custom carousel components?
Custom carousel components aren’t easy to maintain, and your teams will find it hard to maintain such components with growing requirements. Hence, if you want peace of mind, it is much better to use ready-made libraries.







